Flanges.
What Are Flanges?
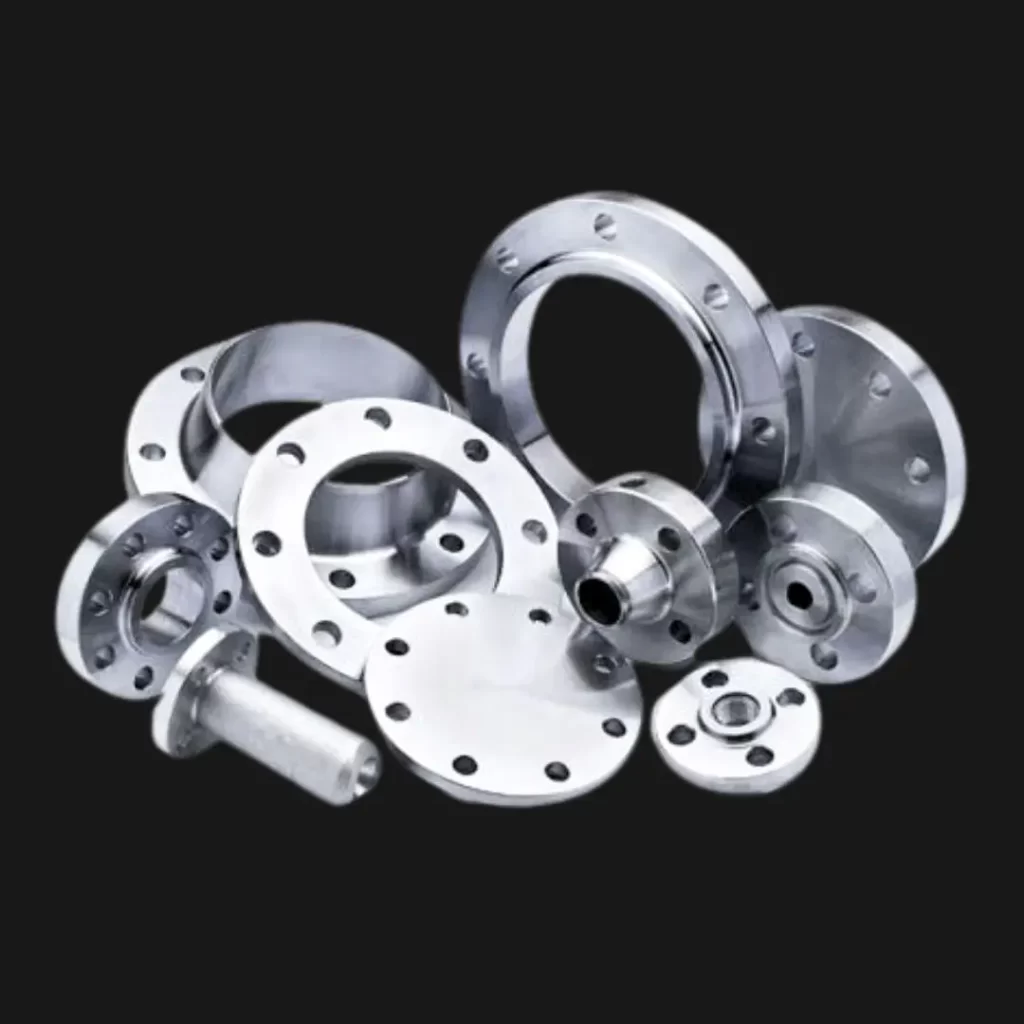
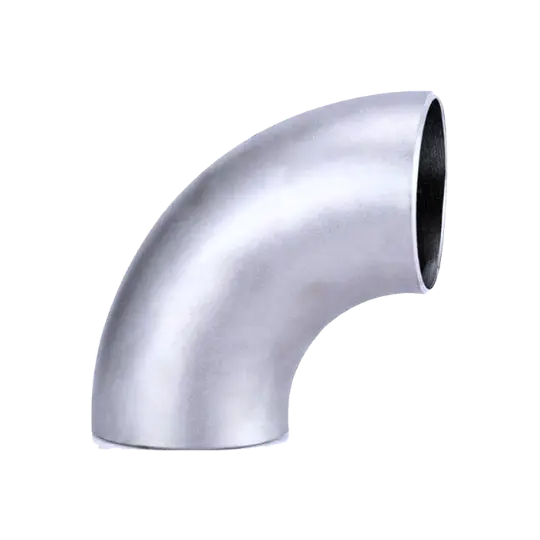
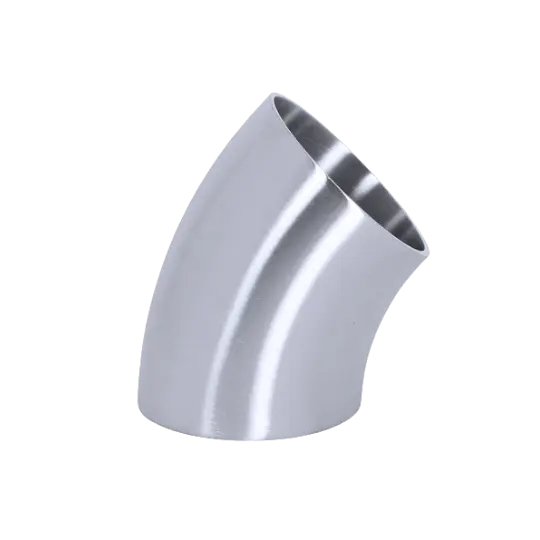
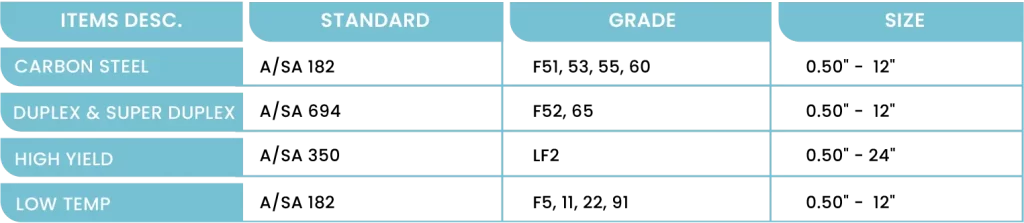
Flanges are forged, disc-shaped mechanical components used to create strong, detachable connections in piping systems designed to ASME/ANSI or DIN standards. Flanges feature precision-drilled bolt holes around their circumference, allowing secure connections between pipes, valves, pumps, and pressure vessels.
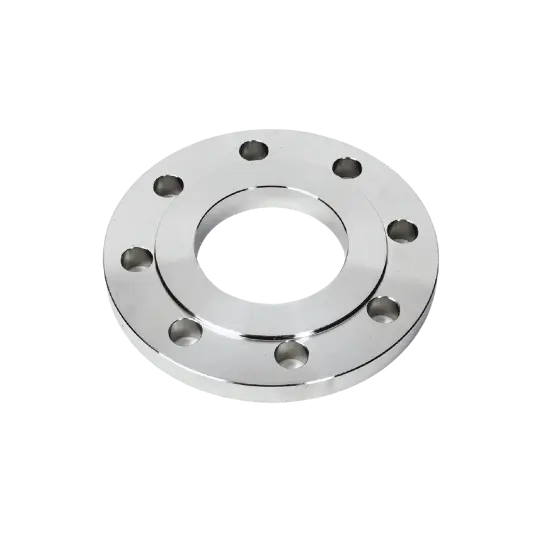
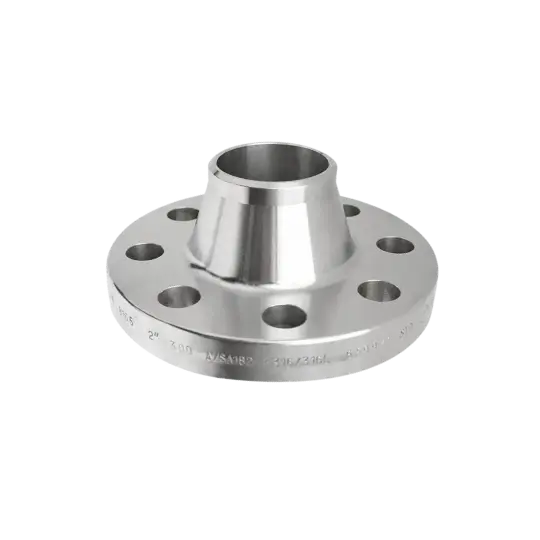
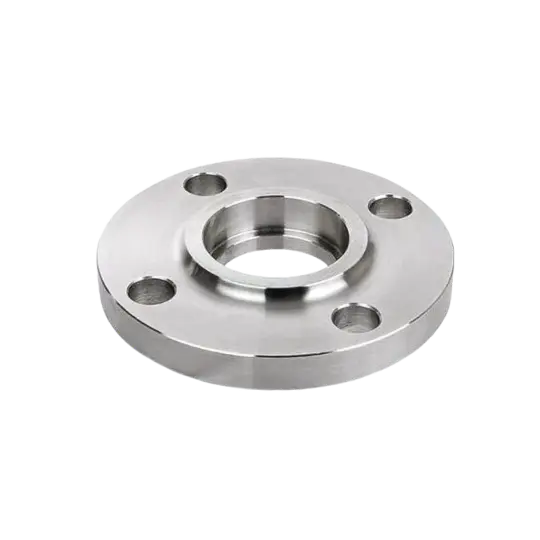
Available in various types including weld neck, slip-on, socket weld, and blind flanges, they provide a reliable and practical solution for industrial piping connections.
Advantages of Flanges?
Easy maintenance and accessibility
Enables quick disassembly for inspections, cleaning, and replacement of equipment without cutting pipes or damaging the system
Versatile Applications
Compatible with various piping materials and pressure ratings, making them ideal for a wide range of industrial applications
Leak-proof & Secure Sealing
Designed to create secure, leak-tight connections while maintaining system integrity under various operating conditions.
Cost-effective & Reusable
Reduces downtime and maintenance cost by offering a reusable, long-term connection solution.
Brands We Carry.







Fill out the form, and our team will get back to you within 24 hours.
Submit Your Inquiry.